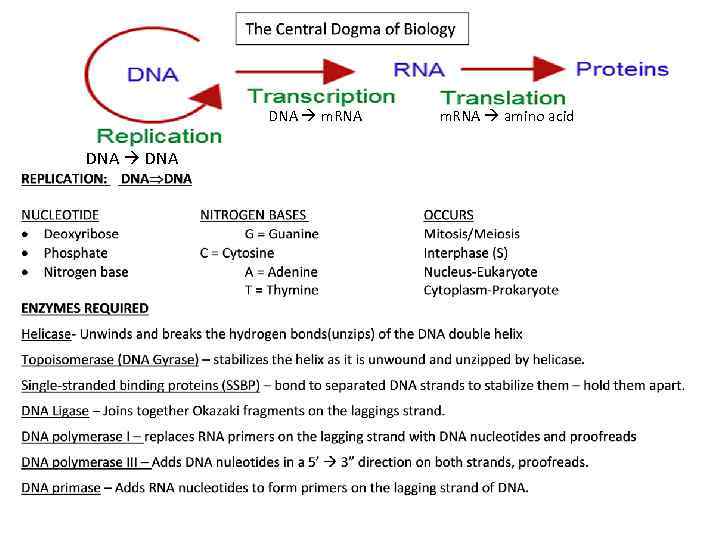
That pol i stands for dna polymerase i and pol iii stands for dna
Home » Query » That pol i stands for dna polymerase i and pol iii stands for dnaYour That pol i stands for dna polymerase i and pol iii stands for dna images are ready in this website. That pol i stands for dna polymerase i and pol iii stands for dna are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Get the That pol i stands for dna polymerase i and pol iii stands for dna files here. Find and Download all free photos.
If you’re searching for that pol i stands for dna polymerase i and pol iii stands for dna images information related to the that pol i stands for dna polymerase i and pol iii stands for dna keyword, you have come to the right blog. Our website always provides you with suggestions for seeking the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly surf and find more enlightening video articles and images that fit your interests.
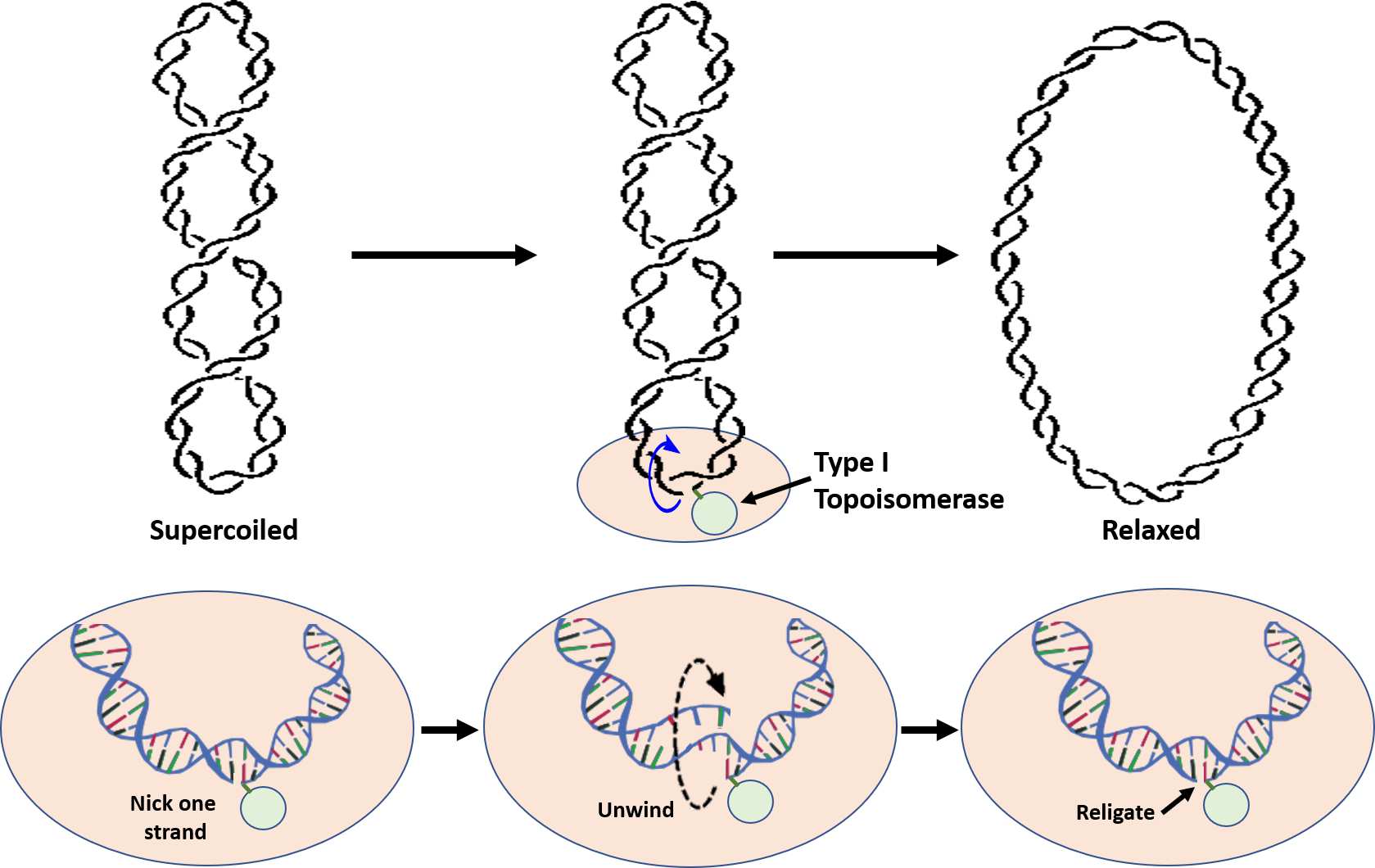
That Pol I Stands For Dna Polymerase I And Pol Iii Stands For Dna. Pol I is much less processive than Pol III because its primary function in DNA replication is to create. In other words after replication there will be two new daughter DNA strands which carry the same genetic information with the original DNA strand. In DNA replication in bacteria the enzyme DNA polymerase III abbreviated DNA pol III adds nucleotides to a template strand of DNA. The only role of DNA polymerase I is to hydrolyse the RNA primer and fill in the gaps with complementary deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates and the end of DNA replication.
 Electron Micrographs Of Dna Molecules After Unwinding With T Antigen Download Scientific Diagram From researchgate.net
Electron Micrographs Of Dna Molecules After Unwinding With T Antigen Download Scientific Diagram From researchgate.net
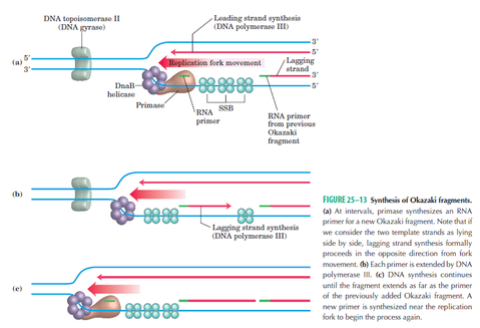
DNA Pol I has a 5 to 3 exonuclease activity in addition to its polymerase activity and uses its exonuclease activity to degrade the RNA primers ahead of it as it extends the DNA strand behind it in a process called nick translation. DNA polymerase I pol I processes RNA primers during lagging-strand synthesis and fills small gaps during DNA repair reactions. But DNA pol III cannot start a new strand from scratch. DNA polymerase III has 3 functions. Each of the four images below shows a strand of template DNA dark blue. It performs the 5-3 polymerase function which means that it adds nucleotides to the 3 end of the forming DNA strand during replication.
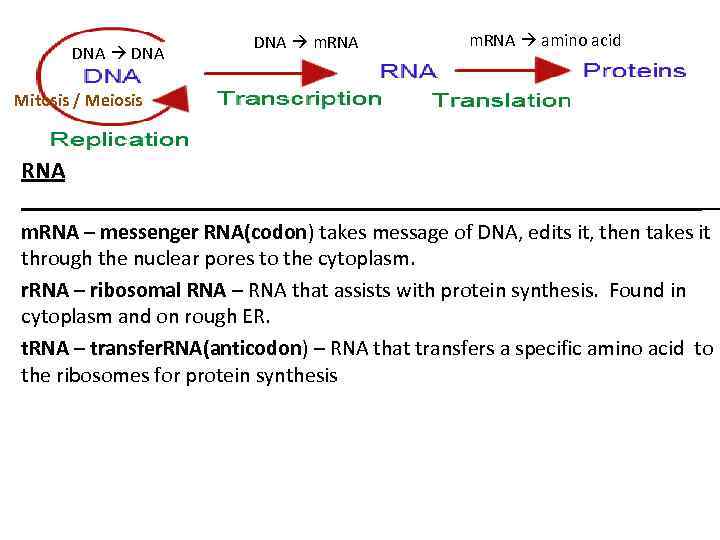
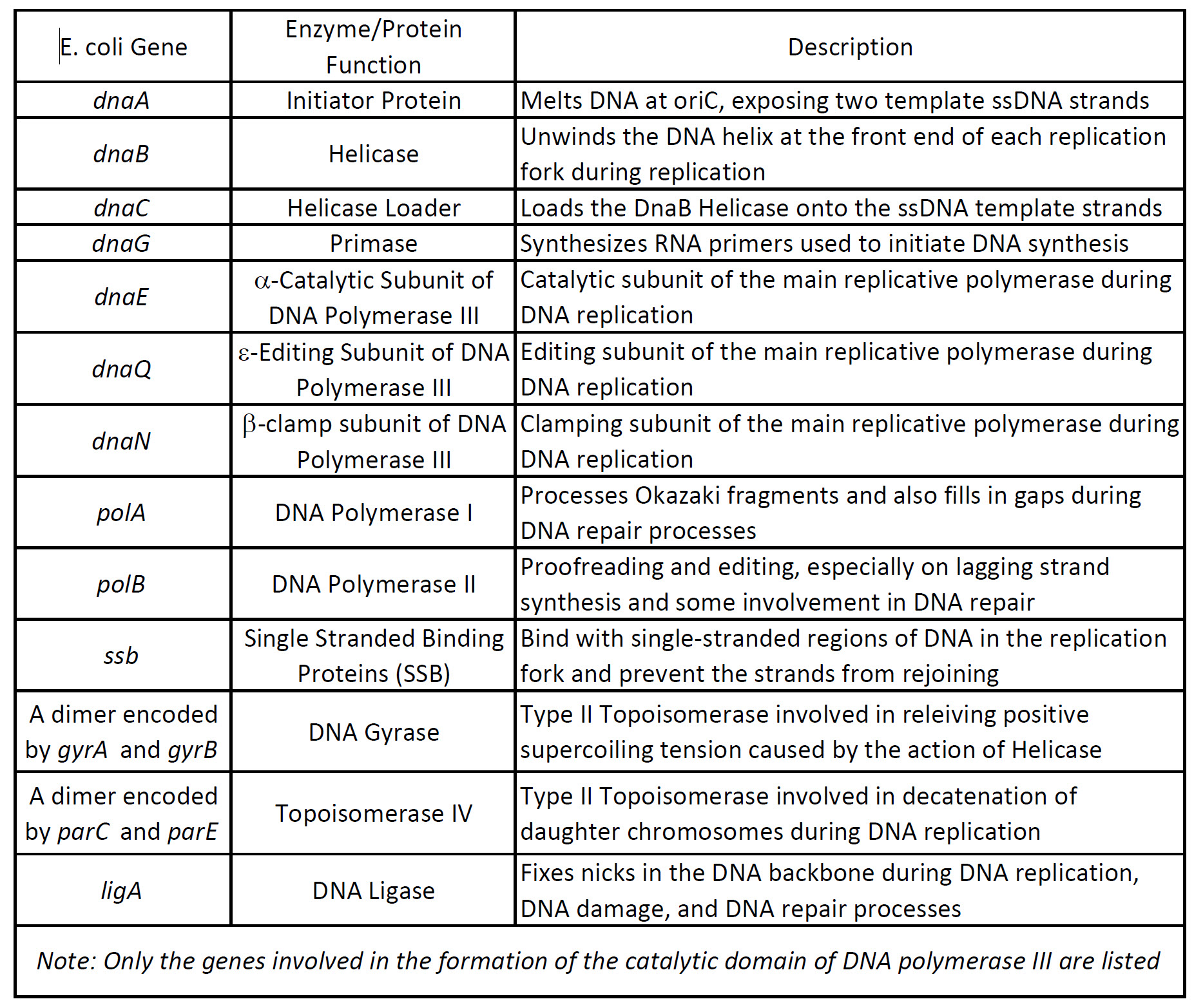
Viruses have only 1 DNA pol prokaryotes have 5 DNA pol DNA polymerase I II III IV and V and eukaryotes have 15 DNA pol designated with greek letters as DNA pol α 𝛃 𝛄 ẟ ε ζ η θ ι 𝛋 λ.
Pol I is much less processive than Pol III because its primary function in DNA replication is to create. During the replication the DNA polymerase always. But DNA pol III cannot start a new strand from scratch. As a result Pol I does not have to be nearly as processive as Pol III. Here we address these questions by analyzing pol I mutations generated through error-prone replication of ColE1. Its main function is to replicate new DNA strands from an original DNA strand.
 Source: present5.com
Source: present5.com
DNA pol I DNA pol II and DNA pol III. Here we address these questions by analyzing pol I mutations generated through error-prone replication of ColE1. Viruses have only 1 DNA pol prokaryotes have 5 DNA pol DNA polymerase I II III IV and V and eukaryotes have 15 DNA pol designated with greek letters as DNA pol α 𝛃 𝛄 ẟ ε ζ η θ ι 𝛋 λ. In DNA replication in bacteria the enzyme DNA polymerase III abbreviated DNA pol III adds nucleotides to a template strand of DNA. In other words after replication there will be two new daughter DNA strands which carry the same genetic information with the original DNA strand.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
DNA polymerase 3 is essential for the replication of the leading and the lagging strands whereas DNA polymerase 1 is essential for removing of the RNA primers from the fragments and replacing it with the required nucleotides. However it is unclear how pol I and pol III work together during replication and repair or how extensive pol I processing of Okazaki fragments is in vivo. Fragment B will be synthesized next in the space between primers A and B. DNA Polymerase I Pol I catalyzes the incorporation of dNTPs into double-stranded DNA in a 53 direction that is complementary to the DNA or RNA template strand. Selects and adds free deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates complementary to the DNA template strand.
 Source: wou.edu
Source: wou.edu
Note that pol I stands for DNA. But DNA pol III cannot start a new strand from scratch. IIHH primer A fragment A space for fragment B 3 primer B replication fork Adapted from vagy by Campbell and Recce 2008 Pearson Education Inc. As a result Pol I does not have to be nearly as processive as Pol III. DNA polymerase III has 3 functions.
 Source: wou.edu
Source: wou.edu
More complex cells possess more DNA polymerases. As a result Pol I does not have to be nearly as processive as Pol III. DNA pol III is the enzyme required for DNA synthesis. Here we address these questions by analyzing pol I mutations generated through error-prone replication of ColE1. In DNA replication in bacteria the enzyme DNA polymerase III abbreviated DNA pol III adds nucleotides to a template strand of DNA.
 Source: wou.edu
Source: wou.edu
During the replication the DNA polymerase always. DNA polymerase III has 3 functions. DNA polymerase 3 is essential for the replication of the leading and the lagging strands whereas DNA polymerase 1 is essential for removing of the RNA primers from the fragments and replacing it with the required nucleotides. DNA pol I DNA pol II and DNA pol III. Drag the labels to their appropriate locations in the flowchart below indicating the sequence of events in the production of fragment B.
 Source: wou.edu
Source: wou.edu
It performs the 5-3 polymerase function which means that it adds nucleotides to the 3 end of the forming DNA strand during replication. DNA Pol I has a 5 to 3 exonuclease activity in addition to its polymerase activity and uses its exonuclease activity to degrade the RNA primers ahead of it as it extends the DNA strand behind it in a process called nick translation. Here we address these questions by analyzing pol I mutations generated through error-prone replication of ColE1. In DNA replication in bacteria the enzyme DNA polymerase III abbreviated DNA pol III adds nucleotides to a template strand of DNA. They do this by adding individual nucleotides to the 3-prime hydroxl group of a strand of DNA.
 Source: jbc.org
Source: jbc.org
Pol I is much less processive than Pol III because its primary function in DNA replication is to create. Here we address these questions by analyzing pol I mutations generated through error-prone replication of ColE1. DNA Polymerase I Pol I catalyzes the incorporation of dNTPs into double-stranded DNA in a 53 direction that is complementary to the DNA or RNA template strand. DNA polymerases are the enzymes that replicate DNA in living cells. Viruses have only 1 DNA pol prokaryotes have 5 DNA pol DNA polymerase I II III IV and V and eukaryotes have 15 DNA pol designated with greek letters as DNA pol α 𝛃 𝛄 ẟ ε ζ η θ ι 𝛋 λ.
 Source: present5.com
Source: present5.com
Note that pol I stands for DNA. More complex cells possess more DNA polymerases. However it is unclear how pol I and pol III work together during replication and repair or how extensive pol I processing of Okazaki fragments is in vivo. The process uses a complementary single strand of DNA as a template. Instead a primer must pair with the template strand and DNA pol III then adds nucleotides to the primer complementary to the template strand.
 Source: wou.edu
Source: wou.edu
It possesses 35 exonuclease proofreading activity as well as 53 exonuclease activity making the enzyme useful for DNA end blunting and DNA labeling by nick translation. DNA Polymerase I Pol I catalyzes the incorporation of dNTPs into double-stranded DNA in a 53 direction that is complementary to the DNA or RNA template strand. Each of the four images below shows a strand of template DNA dark blue. DNA polymerase 3 is essential for the replication of the leading and the lagging strands whereas DNA polymerase 1 is essential for removing of the RNA primers from the fragments and replacing it with the required nucleotides. IIHH primer A fragment A space for fragment B 3 primer B replication fork Adapted from vagy by Campbell and Recce 2008 Pearson Education Inc.
 Source: wou.edu
Source: wou.edu
Drag the labels to their appropriate locations in the flowchart below indicating the sequence of events in the production of fragment B. DNA pol III is the enzyme required for DNA synthesis. DNA Polymerase Structures. In DNA replication in bacteria the enzyme DNA polymerase III abbreviated DNA pol III adds nucleotides to a template strand of DNA. IIHH primer A fragment A space for fragment B 3 primer B replication fork Adapted from vagy by Campbell and Recce 2008 Pearson Education Inc.
 Source: reasonandscience.catsboard.com
Source: reasonandscience.catsboard.com
DNA Pol I has a 5 to 3 exonuclease activity in addition to its polymerase activity and uses its exonuclease activity to degrade the RNA primers ahead of it as it extends the DNA strand behind it in a process called nick translation. As a result Pol I does not have to be nearly as processive as Pol III. These enzymes cannot replace each other as. They do this by adding individual nucleotides to the 3-prime hydroxl group of a strand of DNA. Drag the labels to their appropriate locations in the flowchart below indicating the sequence of events in the production of fragment B.
 Source: wou.edu
Source: wou.edu
Viruses have only 1 DNA pol prokaryotes have 5 DNA pol DNA polymerase I II III IV and V and eukaryotes have 15 DNA pol designated with greek letters as DNA pol α 𝛃 𝛄 ẟ ε ζ η θ ι 𝛋 λ. They do this by adding individual nucleotides to the 3-prime hydroxl group of a strand of DNA. DNA polymerases are the enzymes that replicate DNA in living cells. These enzymes cannot replace each other as. DNA pol III is the enzyme required for DNA synthesis.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
DNA polymerase III has 3 functions. However it is unclear how pol I and pol III work together during replication and repair or how extensive pol I processing of Okazaki fragments is in vivo. Note that pol I stands for DNA polymerase I and pol III stands for DNA polymerase III step 5 after pol I replaces primer A with DNA. But DNA pol III cannot start a new strand from scratch. DNA polymerase I pol I processes RNA primers during lagging-strand synthesis and fills small gaps during DNA repair reactions.
 Source: wou.edu
Source: wou.edu
DNA polymerase I pol I processes RNA primers during lagging-strand synthesis and fills small gaps during DNA repair reactions. Selects and adds free deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates complementary to the DNA template strand. Instead a primer must pair with the template strand and DNA pol III then adds nucleotides to the primer complementary to the template strand. Each of the four images below shows a strand of template DNA dark blue. DNA pol I is used later in the process and DNA pol II is used primarily required for repair this is another irritating example of naming that was done based on the order of discovery rather than an order that makes sense.
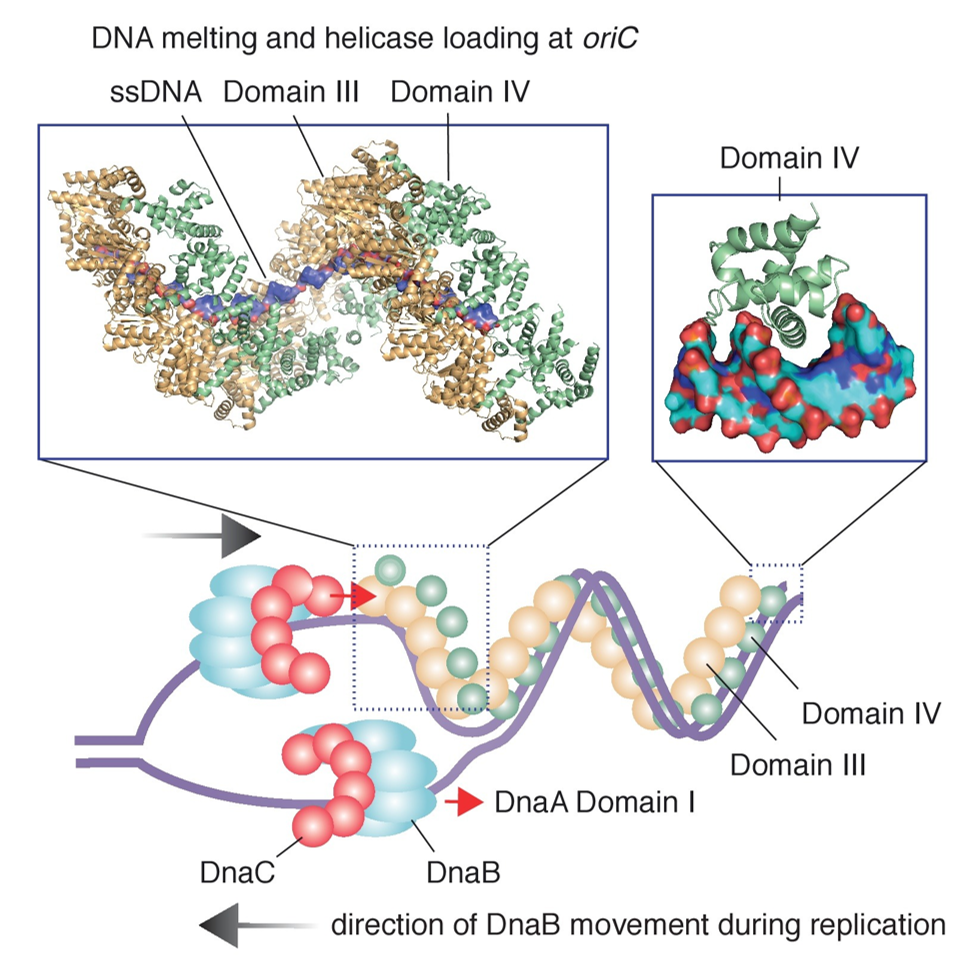 Source: wou.edu
Source: wou.edu
Note that pol I stands for DNA polymerase I and pol III stands for DNA polymerase III step 5 after pol I replaces primer A with DNA. In fact Pol III is the principle enzyme used in Bacterial cells for replicating chromosomal DNA whereas Pol I is used primarily to excise the RNA primer and fill in the resulting single-stranded regions of DNA. It is the primary enzyme responsible for DNA replication in. However it is unclear how pol I and pol III work together during replication and repair or how extensive pol I processing of Okazaki fragments is in vivo. But DNA pol III cannot start a new strand from scratch.
 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
DNA polymerase I pol I processes RNA primers during lagging-strand synthesis and fills small gaps during DNA repair reactions. But whats peculiar about this polymerase is that it is a thermostable enzyme that can stand high-temperature conditions unlike most known enzymes that work properly only at 37C. However it is unclear how pol I and pol III work together during replication and repair or how extensive pol I processing of Okazaki fragments is in vivo. Pol I is much less processive than Pol III because its primary function in DNA replication is to create. In DNA replication in bacteria the enzyme DNA polymerase III abbreviated DNA pol III adds nucleotides to a template strand of DNA.
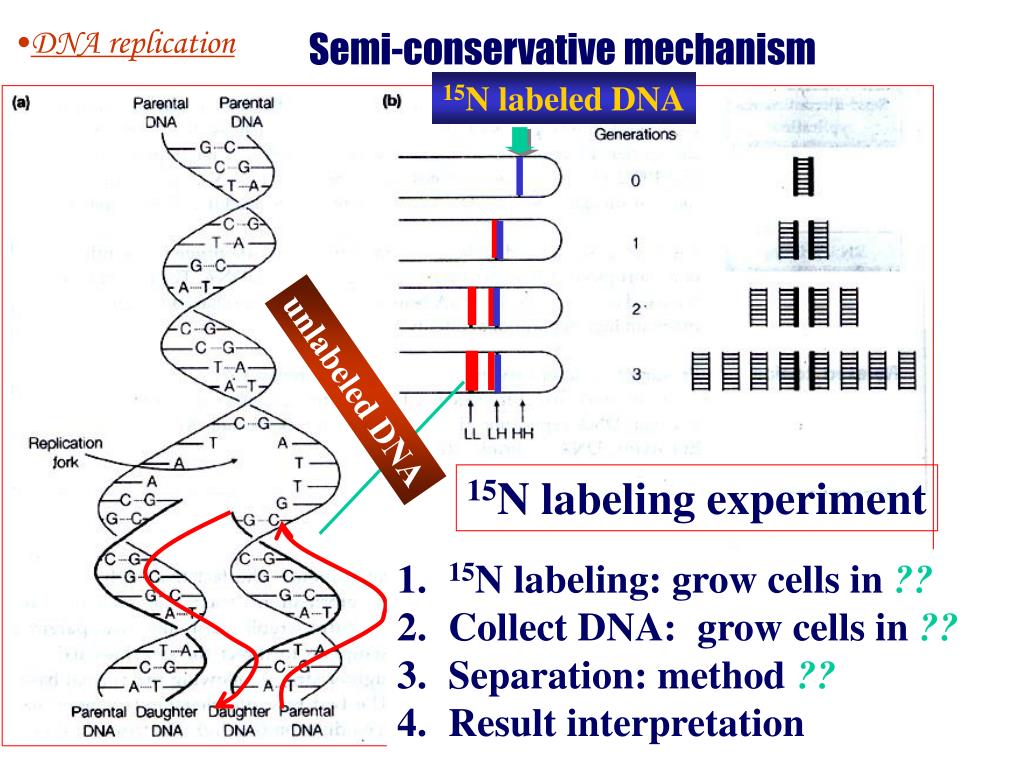 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
It performs the 5-3 polymerase function which means that it adds nucleotides to the 3 end of the forming DNA strand during replication. Each of the four images below shows a strand of template DNA dark blue. The enzyme DNA polymerase III is the primary enzyme involved with bacterial DNA replication. The only role of DNA polymerase I is to hydrolyse the RNA primer and fill in the gaps with complementary deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates and the end of DNA replication. In other words after replication there will be two new daughter DNA strands which carry the same genetic information with the original DNA strand.
 Source: wou.edu
Source: wou.edu
Instead a primer must pair with the template strand and DNA pol III then adds nucleotides to the primer complementary to the template strand. In prokaryotes three main types of polymerases are known. Before replication can start the enzyme helicase unwinds the two DNA strands. But whats peculiar about this polymerase is that it is a thermostable enzyme that can stand high-temperature conditions unlike most known enzymes that work properly only at 37C. DNA pol I is used later in the process and DNA pol II is used primarily required for repair this is another irritating example of naming that was done based on the order of discovery rather than an order that makes sense.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site adventageous, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title that pol i stands for dna polymerase i and pol iii stands for dna by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.